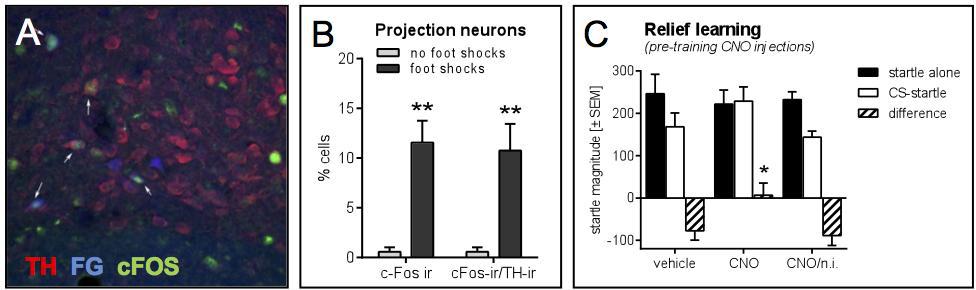
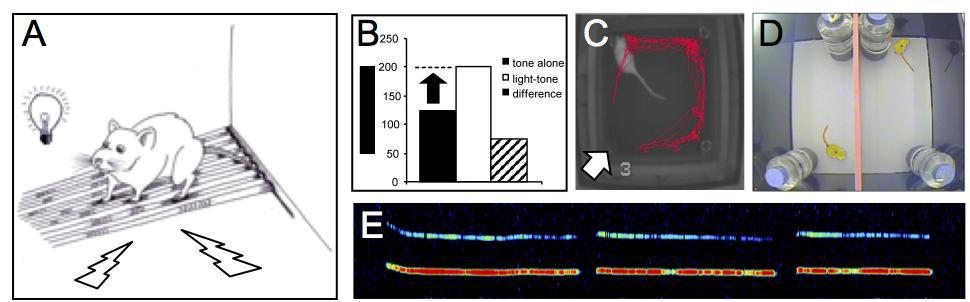
Behavioral paradigms: Animals are exposed to emotionally-relevant stimuli (A) and cues associated with on- or offset of such stimuli can be learned (e.g., fear conditioning). Learned or innate emotionally-relevant stimuli modulate behavior. For example, fear-inducing stimuli can potentiate startle magnitude (B), are avoided (C), reduce sociability (D) and induce alarm calls (E).

Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Markus Fendt
Neuropharmacology of emotional systems
Institut I :